Algorithm Cookbook Algorithm for quick reference
Get interval sum ideone
#include <cstdio>
const int SIZE = 100;
int A[SIZE];
int prefix_sum[SIZE];
int main() {
int N;
scanf("%d", &N);
prefix_sum[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
scanf("%d", A+i);
prefix_sum[i+1] = prefix_sum[i] + A[i];
}
int begin, end;
while (scanf("%d%d", &begin, &end) == 2) {
for (int i = begin; i < end; ++i)
printf("%d ", A[i]);
printf("-> sum = %d\n", prefix_sum[end]-prefix_sum[begin]);
}
return 0;
}
Input
10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
0 1
1 3
2 4
5 8
9 10
Output
1 -> sum = 1
2 3 -> sum = 5
3 4 -> sum = 7
6 7 8 -> sum = 21
10 -> sum = 10
Determine if a specific number is prime ideone
#include <cstdio>
bool is_prime(int x) {
if (x < 4) return (x == 2 or x == 3);
if (x % 2 == 0 or x % 3 == 0) return false;
for (int i = 5; i * i <= x; i += 6)
if ((x % i == 0) or (x % (i+2) == 0))
return false;
return true;
}
int main() {
int bound;
while (scanf("%d", &bound) == 1) {
printf("Primes less than %d :", bound);
for (int i = 0; i < bound; ++i)
if (is_prime(i))
printf(" %d", i);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Input
100
Output
Primes less than 100 : 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29 31 37 41 43 47 53 59 61 67 71 73 79 83 89 97
Online judge
Reference
Breadth-first search ideone
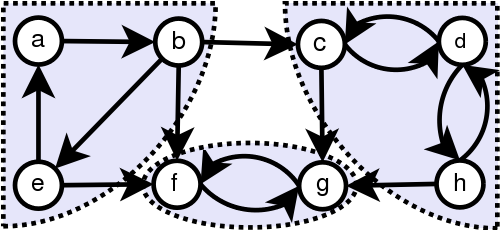 (Graph from wiki)
(Graph from wiki)
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
const int M = 50;
char nodes[M][30];
int pos_node = 0;
std::vector<int> adjacent_nodes[M];
void init() {
pos_node = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) adjacent_nodes[i].clear();
}
int get_node() {
char name[30];
scanf("%s", name);
for (int i = 0; i < pos_node; ++i)
if (!strcmp(name, nodes[i]))
return i;
strcpy(nodes[pos_node++], name);
return pos_node-1;
}
bool bfs(int source, int sink, std::vector<int> & path) {
int enqueued[M], prev[M], distance[M];
memset(enqueued, false, sizeof(enqueued));
memset(distance, 0, sizeof(distance));
std::queue<int> queue;
queue.push(source); enqueued[source] = true; prev[source] = source; distance[source] = 0;
while (not queue.empty()) {
int cur = queue.front(); queue.pop();
if (cur == sink) break;
for (auto next : adjacent_nodes[cur]) {
if (not enqueued[next]) {
queue.push(next); enqueued[next] = true; prev[next] = cur; distance[next] = distance[cur]+1;
}
}
}
path.clear();
if (not enqueued[sink]) return 0;
int now = sink;
while (prev[now] != now) {
path.push_back(now);
now = prev[now];
}
path.push_back(source);
std::reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
return true;
}
void print_path(const std::vector<int> & path) {
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); ++i) {
printf("%s%s", i != 0 ? " -> " : "", nodes[path[i]]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
init();
int n_node;
scanf("%d", &n_node);
for (int i = 0; i < n_node; ++i) {
int from = get_node();
int n_next;
scanf("%d", &n_next);
while (n_next--) {
int to = get_node();
adjacent_nodes[from].push_back(to);
}
}
int n_query;
scanf("%d", &n_query);
while (n_query--) {
std::vector<int> path;
int from = get_node(), to = get_node();
if (bfs(from, to, path))
print_path(path);
else
printf("There is no path from %s -> %s\n", nodes[from], nodes[to]);
}
return 0;
}
Input
8
a 1 b
b 3 c e f
c 2 d g
d 2 c h
e 2 a f
f 1 g
g 1 f
h 2 d g
3
a b
b h
d e
Output
a -> b
b -> c -> d -> h
There is no path from d -> e
0-1 Knapsack Problem ideone
#include <cstdio>
#include <cassert>
#include <algorithm>
const int MAX_NUM_OBJECTS = 30;
const int MAX_NUM_WEIGHTS = 100;
int knapsack[MAX_NUM_OBJECTS+5][MAX_NUM_WEIGHTS+5];
bool knapsack_taken[MAX_NUM_OBJECTS+5][MAX_NUM_WEIGHTS+5];
int knapsack_n_taken[MAX_NUM_OBJECTS+5][MAX_NUM_WEIGHTS+5];
struct Object {
int _weight, _value;
int weight() const { return _weight; }
int value() const { return _value; }
} objects[MAX_NUM_OBJECTS];
void print_object(int nObject, int nWeight) {
if (nObject != 0 and nWeight != 0) {
if (knapsack_n_taken[nObject][nWeight]) {
int cur_object_value = objects[nObject].value();
int cur_object_weight = objects[nObject].weight();
print_object(nObject-1, nWeight-cur_object_weight);
printf(" %d %d\n", cur_object_weight, cur_object_value);
} else {
print_object(nObject-1, nWeight);
}
}
}
int main() {
int max_weight, nObject, posCase = 1;
while (scanf("%d%d", &max_weight, &nObject) == 2) {
assert(max_weight <= MAX_NUM_WEIGHTS);
assert(nObject < MAX_NUM_OBJECTS);
for (int i = 1; i <= nObject; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d", &objects[i]._weight, &objects[i]._value);
assert(objects[i].weight() <= MAX_NUM_WEIGHTS);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= max_weight; ++i) knapsack[0][i] = knapsack_n_taken[0][i] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= nObject; ++i) knapsack[i][0] = knapsack_n_taken[i][0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= nObject; ++i)
for (int k = 1; k <= max_weight; ++k) {
int cur_object_weight = objects[i].weight();
int cur_object_value = objects[i].value();
int prev_value = knapsack[i-1][k];
int reduced_weight = k-cur_object_weight;
int taken_value = cur_object_value + knapsack[i-1][reduced_weight];
knapsack[i][k] = prev_value;
knapsack_taken[i][k] = false;
knapsack_n_taken[i][k] = knapsack_n_taken[i-1][k];
if (k >= cur_object_weight and taken_value > prev_value) {
knapsack[i][k] = taken_value;
knapsack_taken[i][k] = true;
knapsack_n_taken[i][k] = knapsack_n_taken[i-1][reduced_weight] + 1;
}
}
printf("Case #%d\n", posCase++);
printf(" max value : %d\n", knapsack[nObject][max_weight]);
printf(" num of object : %d\n", knapsack_n_taken[nObject][max_weight]);
print_object(nObject, max_weight);
}
return 0;
}
Input
50
3
10 60
20 100
30 120
Output
Case #1
max value : 220
num of object : 2
20 100
30 120
Online judge
Longest Strictly Increasing / Decreasing Subsequence ideone
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
std::vector<int> A, lis, lis_pos, pos_prev;
int last_pos;
void print_prev(int pos) {
if (pos != pos_prev[pos])
print_prev(pos_prev[pos]);
printf("%d ", A[pos]);
}
int main() {
int x;
for (int pos = 0; scanf("%d", &x) == 1; ++pos) {
A.push_back(x);
pos_prev.push_back(pos);
if (lis.size() == 0 or lis.back() < x) {
lis.push_back(x);
lis_pos.push_back(pos);
if (lis.size() > 1)
pos_prev[pos] = lis_pos[lis.size()-2];
last_pos = pos;
} else {
auto it = std::lower_bound(lis.begin(), lis.end(), x);
size_t pos_replace = it - lis.begin();
lis[pos_replace] = x;
lis_pos[pos_replace] = pos;
if (pos_replace > 0)
pos_prev[pos] = lis_pos[pos_replace-1];
if (pos_replace == lis.size()-1)
last_pos = pos;
}
}
print_prev(last_pos);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
The above code computes the LIS and prints the last longest stricly increasing sequence.
Input
8 10 4 13 16 5 3 3 1 13 18 10 2 8 17
Output
8 10 13 16 17
Online judge
(UVA 481 What Goes Up, medium) (UVA 11456 Trainsorting, medium)
Longest Common Subsequence ideone
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
const int MAX_LENGTH = 100;
int A[MAX_LENGTH], B[MAX_LENGTH];
int lis[MAX_LENGTH][MAX_LENGTH];
std::pair<int, int> lis_prev[MAX_LENGTH][MAX_LENGTH];
void print_longest_common_subsequence(int i, int k) {
if (i != 0 and k != 0) {
const auto & pr = lis_prev[i][k];
print_longest_common_subsequence(pr.first, pr.second);
if (pr.first == i-1 and pr.second == k-1)
printf("%d ", A[pr.first]);
}
}
int main() {
int na, nb;
while (scanf("%d", &na) == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < na; ++i) scanf("%d", A+i);
scanf("%d", &nb);
for (int i = 0; i < nb; ++i) scanf("%d", B+i);
memset(lis, 0, sizeof(lis));
for (int i = 0; i < na; ++i)
for (int k = 0; k < nb; ++k) {
if (A[i] == B[k]) {
lis[i+1][k+1] = lis[i][k] + 1;
lis_prev[i+1][k+1] = std::make_pair(i, k);
} else {
if (lis[i+1][k] >= lis[i][k+1]) {
lis[i+1][k+1] = lis[i+1][k];
lis_prev[i+1][k+1] = std::make_pair(i+1, k);
} else {
lis[i+1][k+1] = lis[i][k+1];
lis_prev[i+1][k+1] = std::make_pair(i, k+1);
}
}
}
printf("lcc length : %d\n", lis[na][nb]);
print_longest_common_subsequence(na, nb);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Input
8
1 3 2 4 3 5 4 6
4
3 4 5 6
Output
lcc length : 4
3 4 5 6
Online judge
(UVA 531 Compromise, elementary)
Challenges
| Dynamic programming | Difficulty | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Algospot QUANTIZE | hard | Good problem to test a problem can be solved by its sub-problem | github |
| Combinatorial search | Difficulty | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| POJ 2676 - Sudoku | simple | Constraint satisfaction problem, learn how to do constraint propogation efficiently | github |
| Algospot KAKURO2 | intermediate | Constraint satisfaction problem, learn how to do constraint propogation efficiently | github |
| Maximum flow | Difficulty | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| UVA 820 - Internet Bandwidth | elementary | undirected graph | github |
| UVA 10330 - Power Transmission | simple | directed graph, capacity constraints on node | github |
| Breadth-first search | Difficulty | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 314 - Robot | intermediate | Record visited path not only x and y, but also orientation | github |